What is Blockchain Technology: Everything You Need to Know
Table of Contents
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a distributed-ledger-based computer-generated network that fosters decentralization and avoids single-point failure of any network. It is a record-keeping technology that stores information and transaction data in blocks, which are very hard to hack and provide enhanced security. The data stored on a blockchain is immutable, which means data from one block cannot be altered by changing the data in other blocks. It makes blockchain technology more secure and transparent than centralized networks. Most blockchains use a consensus mechanism to approve the transactions, such as the proof of stake (PoS) mechanism, the proof of work (PoW) mechanism, and the proof of authority (PoA) mechanism. Bitcoin uses the PoW mechanism, whereas Ethereum 2.0 uses the PoS mechanism.
The Significance of Blockchain in Today’s World
When we hear the word ‘Blockchain’, we think about cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, which is not wrong because blockchain technology is the underpinning of the cryptocurrency landscape. However, other than cryptocurrency, blockchain is highly significant in multiple sectors, such as supply chain management, real estate, and healthcare data management. Blockchain technology is immensely significant in today’s dynamic era because of three main factors: Disintermediation, Transparency and Inception.
Disintermediation means there are no intermediaries present to validate the transactions. The individuals on the network, also known as nodes, are the sole decision-makers and validate the transactions by consensus mechanisms. Since the blockchain is immutable and every node keeps a record of each transaction, the chances of any data breach are low. Hence, transparency is greatly enhanced. Blockchain technology is a record-keeping architecture, and one of the most significant facts about blockchain is that it keeps a record of every transaction of each asset or information since the inception of the transaction.
Blockchain technology is playing a pivotal role in the banking sector by fostering financial inclusion, Peer-to-peer transactions and global accessibility.
The Future of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has already proved its worth and the wonders it can do in multiple sectors. It has revolutionized the financial landscape. It is changing the global payment scenario by enabling people to pay in cryptocurrencies across borders without worrying about currency exchange. In the past few months, multiple countries have issued cryptographically secure digital currencies, and many countries are going to do that in upcoming months. In future, blockchain technology will be adopted by all the central banks around the world to enhance cyber security and transparency in the system. Blockchain technology is here to rule the future and empower other technologies.
The Market Size of Blockchain Technology
The global market size of the blockchain technology market was valued at 28 billion USD in 2024, and it is projected to grow with a CAGR of at least 50% as per the market reports. It is poised to touch USD 800 billion by 2032.
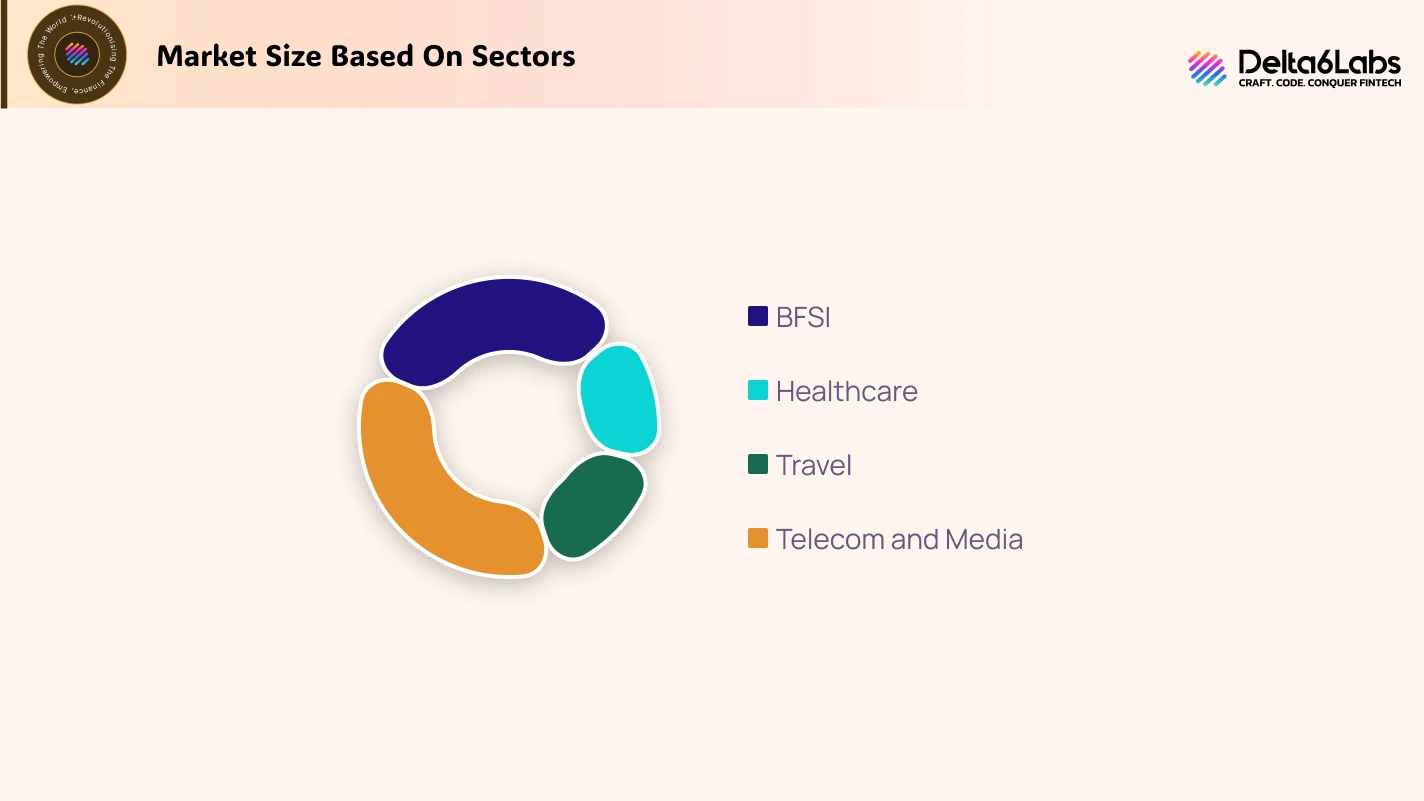
If we look at the market share of blockchain, based on sectors, then the BFSI sector has the highest share, followed by the telecom and media sectors.
Types of Blockchain
Public blockchain
Public blockchains completely follow the process of decentralisation, they are permissionless distribution systems and do not have any restrictions. These are not owned by anyone, every node on the network can participate in the consensus mechanism. Public blockchains are secure and anonymous. Bitcoin and Ethereum are two main examples of public blockchains.
Private blockchain
Private blockchains are like public blockchains in their functionality, except these blockchains are used for smaller and restricted networks. These are permission blockchains that are operative in a closed network. These blockchains resolve the issue of scalability and foster privacy.
Hybrid blockchain
Hybrid blockchains are a blend of both private and public blockchains. The ownership and accessibility can be fractional in hybrid blockchains, some parts of the network are accessible to everyone and others to the organization only. These blockchains are cost-effective and provide customization. XinFin is an example of a hybrid blockchain.
Consortium Blockchain
A consortium blockchain works on a semi-decentralized module in which more than one organization manages a blockchain. The cost and risk are shared among the participants, which makes a consortium blockchain highly efficient and affordable. These types of blockchains foster a collaborative approach and cross-organizational coordination.
The Working Mechanism of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology’s working mechanism follows the following four key concepts: consensus mechanism, distributed ledger, smart contracts and permissions. But before we learn about these concepts, we must understand some basic terminology about blockchain, such as:
Node: Any individual in the network that is taking part in the transaction or validating a transaction is called a node.
Hash: Each blockchain has a hash, which means a digital and unique identification has been done for the transactions. A hash is a unique alphanumeric code. They link the blocks together and make sure that no other block is added to the network without authentication. Hence, they make blockchain networks tamperproof.
Node and Hash are two commonly used terms in the working of blockchain technology. As the name suggests, ‘blockchain’ is a network of blocks that stores data or information. Each block has a unique alphanumeric code, which is cryptographically generated and works as a digital fingerprint known as a hash. These Hash play a critical role in linking the blocks in a chronological sequence.
If a new transaction takes place, it is validated by the nodes. Multiple nodes can take part in the validation process, depending on the consensus mechanism. Once the validation has taken place, a new block is added to the open end of the network. The validator also receives some percentage of the amount as a reward for validating the transaction. The details of the transactions, such as transaction date, name of the validator node and amount, are stored on the network permanently and are immutable.
Components of Blockchain Technology
Consensus Mechanism
One of the most important concepts of blockchain technology is the consensus mechanism. It validates whether the transaction has taken place or not. Blockchains use various consensus mechanisms like the Proof of Stake, Proof of Work, and Proof of Authority mechanisms. Bitcoin works on the PoW mechanism, but it has some disadvantages. It consumes very high energy and is not eco-friendly. On the other hand, Ethereum 2.0 uses the PoS mechanism, which consumes less energy than the PoW mechanism.
Distributed Ledger
Blockchain operates as a shared ledger that records all transactions; these transactions are secure and immutable.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are one of the most significant parts of blockchain technology. Smart contracts bring transparency and foster intermediation. Smart contracts are digital contracts that can execute themselves automatically when the predetermined terms and conditions are satisfied. Smart contracts ensure smooth and secure credit and withdrawal of digital assets without any human interference.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has numerous benefits in various sectors, including education, health, supply chain, real estate, media and banking. However, it is important to understand why these sectors are moving from traditional systems to blockchain technology. In this section, we will learn about the benefits blockchain provides:
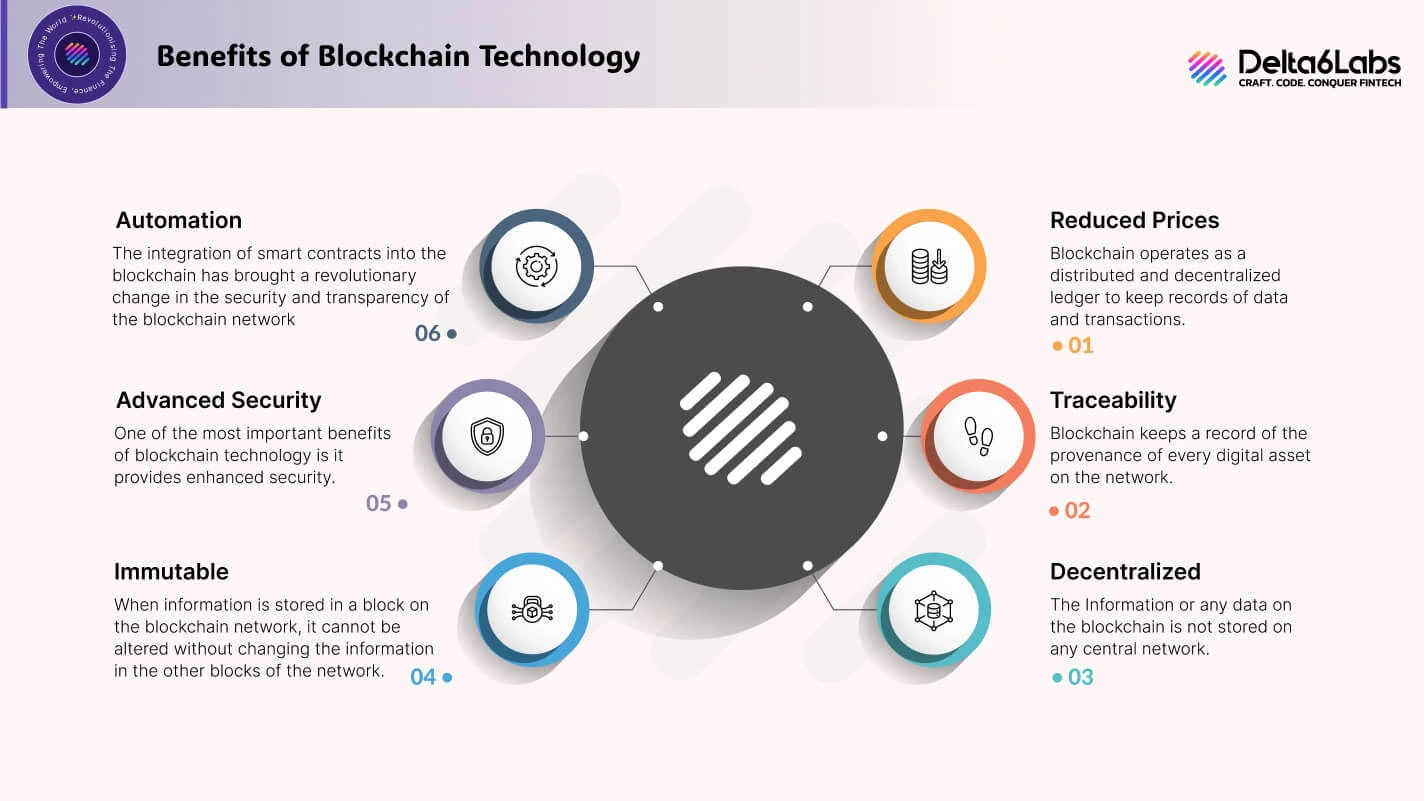
Reduced Prices
Blockchain operates as a distributed and decentralized ledger to keep records of data and transactions. Most of the functions are automatically executed, and there is no organizational structure or central entity present. There is no infrastructural cost also. It automatically brings down the total price.
Traceability
Blockchain keeps a record of the provenance of every digital asset on the network. Every individual can see the journey of any asset on the network for proof checking. In supply chain management, the Traceability feature of blockchain has been proven highly beneficial.
Decentralized
The Information or any data on the blockchain is not stored on any central network. Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, and every peer has access to all the information stored on the blockchain. As there is no central entity, all the decisions are made by the participants.
Immutable
When information is stored in a block on the blockchain network, it cannot be altered without changing the information in the other blocks of the network. Once any fact is stored, then it remains forever on the network. It makes blockchain a transparent network.
Advanced Security
One of the most important benefits of blockchain technology is it provides enhanced security. The hashes used in blockchain are unique and cryptographically generated, these hashes make the blockchain tamper-proof and highly secure.
Automation
The integration of smart contracts into the blockchain has brought a revolutionary change in the security and transparency of the blockchain network. Smart contracts are designed to execute themselves automatically when the predetermined conditions are met. Hence, they reduce human interference and thus improve transparency.
Limitations of Blockchain Technology
Illegal Activities
One of the most criticized things about the blockchain is it can be used to share illegal and highly sensitive information without being tracked by any central or regulatory entity.
Scalability
Scalability is also a big limitation of the blockchain. A block can also store up to 1 MB due to which only a few transactions are possible.
Environmental Concerns
Blockchain consumes a lot of energy for validating a transaction; environmental activists have termed this as a hazard to sustainable development and SDG goals. The carbon footprints and water footprints of Bitcoin mining, which takes place on the blockchain network, are also alarmingly high. Cryptocurrency mining consumes the same energy as consumed by nations like Poland and Switzerland.
Regulatory Framework
In the absence of a stringent regulatory network worldwide, there is no authority to oversee problems related to consumer grievances in case of cyber fraud and other potential risks. Also, the energy consumption by Bitcoin miners is not always reported, which leads to creating troubles for the residents. A strong, sustainable policy is required for cryptocurrency miners.
Privacy Issues
The blockchain network is a public network; every individual has access to all the information stored in the blocks. That is beneficial in some respects, but it’s a double-edged sword, it raises serious privacy concerns.
Use Cases of Blockchain Technology
Smart Contracts
These are the applications used on blockchain technology to automate the processing of functions like credits and withdrawals. Smart contracts are secure, reliable, immutable and provide transparency.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Blockchain secures the systems based on the Internet of Things (IoT) with its consensus mechanisms. The data stored on the blockchain is protected by multiple encryptions which are secured by private and public keys.
Cryptocurrency
The digital economy has been revolutionized by cryptocurrencies and these digital currencies are minted on the blockchain. Not just organizations, but individuals also can mint their cryptocurrencies and use them to trade.
NFTs
Non-fungible tokens, popularly known as NFTs, are one of the most important use cases of blockchain technology. NFTs have paved the way for a new revenue stream for artists and musicians. NFTs have also enabled the facility of fractional ownership of digital assets. With the help of NFTs, anything, even a piece of an apple can also become a digital asset.
Banking
The sector that has benefited most since the provenance of blockchain is the banking sector. Blockchain technology has played an integral role in financial inclusion.
Healthcare
Healthcare data related to the patients and the logistics can be stored on the distributed ledger system, that is, blockchain. Healthcare data management has become more secure, transparent and easy with the help of the blockchain network.
Real Estate
Smart contracts, which are operated on the blockchain, can instantly transfer the power of attorney of any property as soon as the decided money is credited. It saves time and brings more transparency to the real estate industry.
Final Words
In the FinTech sector, blockchain has already become a pinnacle even though it is still in its infancy. Its global accessibility has made it famous in every corner of the world. Almost every industry in the world is benefiting from blockchain technology, whether it is banking or real estate, every sector is including blockchain networks in their system because it provides enhanced security, reliability, accessibility, reduced costs, better efficiency, anonymity and transparency than the traditional record-keeping systems.
Blockchain technology has some limitations, including scalability, privacy, interoperability, infrastructure, high equipment cost and some environmental concerns. However, experts are trying to resolve these issues as soon as possible to make the blockchain network more reliable and trustworthy.
The global market of blockchain is growing with a tremendous CAGR. The prospects for the blockchain market are very promising; it is projected to touch the USD 1000 billion mark by the year 2035. In simple words, blockchain is the future of the global economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Disclaimer:
The information on this blog is for knowledge purposes only. The content provided is subject to updates, completion, verification, and amendments, which may result in significant changes.
Nothing in this blog is intended to serve as legal, tax, securities, or investment advice of any investment or a solicitation for any product or service.






